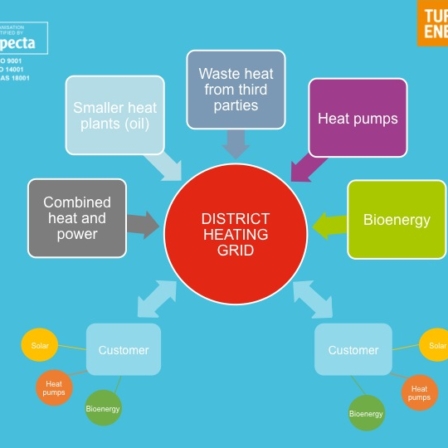
Two-way district heating
Can customers also become producers in the heating market? We studied how an open district heating market could work in Finland.
Competition for customers in the heating market has become much more intense in recent years. This is due to the technological development of different forms of heat production, as well as Finland’s current energy policy and building regulations. District heating companies must actively develop their operating models and seek the most competitive heat production and procurement methods possible.
One possibility is to start developing the heating market towards two-way heat trading. Two-way heat trade refers to a situation in which the district heating company opens up its network to the heat generated by customers or third parties.
What was achieved?
We studied two-way heat trading and investigated different market models for the purchase, by district heating networks, of small-scale heat production and customers’ excess heat. The study helps district heating companies to create the basis for establishing two-way trade, thereby improving the ability of the district heating sectors to respond to the growing climate challenge and expand the heating market’s customer-oriented approach.
The project explored the roles of the different parties, their revenue logic and the interests involved in two-way heat trading. The report (available in Finnish only) answers the following key questions.
- What kind of market and operating models can be used to implement two-way heat trading?
- What are the key requirements for pricing and contracts?
- How can it be ensured that two-way heat trade leads to a solution appropriate for customers, the environment, society and operators?
- What financial perspectives need to be taken into account, and what are the key benefits and disadvantages of two-way heat trade?
- What kinds of customers and customer groups are there?
- What should be taken into account from the perspective of the existing district heating system?
- In what respects will two-way heat trading lead to greater competition in the heating market?
- What kinds of steering methods could be used to promote two-way heat trading?
- What kinds of experiences and research on the subject are available in other countries?
Who participated?
The project involved a separate general study funded by Finnish Energy (ET) and Sitra, as well as a company-specific case study funded by Turku Energia. Both studies were implemented by Pöyry.
LATEST
Interesting viewpoints to this project


WHAT IS IT ABOUT?
Closed project: January to October 2016